Definition
It may be easy to associate magazine media with the traditional print format, but in the last decade magazine media brands have evolved into full multi-platform offerings which span print, digital editions, apps, desktop, mobile, social media, radio, video and TV and even live events. Magazine media are increasing defined by content rather than platform. From this perspective, magazine media are best described as professionally edited, original content that focuses on a particular passion point shared by the brand and the reader.
Where to start
Magazine media continue to enjoy substantial reach in developed nations. In the US, where consumers tend to purchase magazines on an annual subscription basis, the Magazine Publishers of America (MPA) reports that magazine media reach more than 90% of the population. In the UK, The Publishers Audience Measurement Company (PAMCo) reports reach at 72% of the population. Many will be surprised, however, to learn that millennials are more likely to be consuming magazine media than their older counterparts in both these markets. In the US, magazine media reaches 95% of millennials and the UK this figure stands at 76%
The total penetration amongst millennials is of course supported by their use of magazine media on mobile devices, yet print readership amongst this age group remains robust and comparable to older age groups.
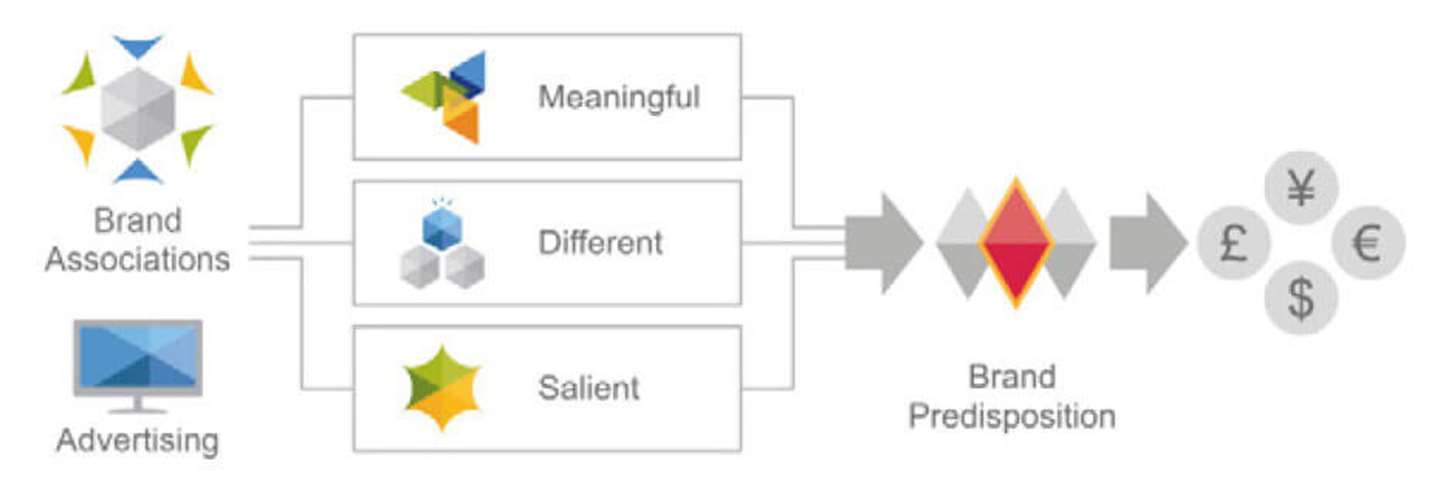
Reach is, however, of secondary importance when planning magazine media because it is magazine media’s ability to deliver highly engaged, highly targeted audiences with little wastage that makes them an essential part of the modern media mix. Due to magazine media’s highly selective content approach (i.e. specialisation in a particular topic or range of related topics with a high level of relevance to the reader’s interests), magazine media are, in effect, self-targeting by nature.
Due to the high level of personal relevance that magazine media content provides, the magazine media reading occasion, particularly in print, it is a deeply engaging and immersive experience which enjoys the full attention of the reader. Various neuroscience studies have confirmed the depth of this reading experience and have shown that magazine media is highly adept at stimulating the three key drivers of long-term memory encoding: narrative, emotion and personal relevance.
In fact, the process of long-term memory encoding (essential to the ability to recall messages at a later date) begins almost immediately once a consumer starts reading a magazine. Of particular importance for advertisers is that long-term memory encoding extends beyond editorial content and applies to advertising as well. This confirms at a neurological level the findings from Magnetic Media’s Moments that Matter study which shows that magazine media offer the highest levels of advertising receptiveness of all channels.